
In today's competitive job market, ensuring fair pay and maintaining a company's competitiveness is crucial for attracting and retaining talent. How can organizations ensure they are compensating their employees fairly and in line with industry standards? The answer lies in understanding "what is compa ratio" – a powerful metric that evaluates employee compensation by comparing their salary to the industry standard midpoint. By understanding and leveraging compa-ratios, companies can establish fair compensation structures and address pay disparities.
Through this guide, we will explore the concept of "what is a compa ratio", its purpose, how to calculate and analyze it, and its application in compensation strategies. We will also touch upon alternative methods for measuring pay competitiveness, providing a well-rounded understanding of how to maintain pay equity and competitiveness in your organization.
Related:
Compa Ratio – The Ultimate Guide and Tutorial
Key Takeaways
- Compa-Ratio is a metric used to evaluate employee compensation against the industry standard and assess pay equity.
It can be used in performance appraisals, budgeting, remuneration policies and salary ranges to ensure fair compensation for employees.
- Alternative methods such as market ratio, target percentile and range penetration are also available to measure pay competitiveness.
Understanding Compa-Ratio

Compa-ratio, short for comparative ratio, is a metric that assesses employee compensation by comparing their salary to the industry standard midpoint. This metric helps organizations understand how an employee's salary aligns with the current market rate and the salaries of similar positions at other organizations. Compa-ratio primarily aids in certifying that employees receive fair and competitive remuneration, assisting organizations in upholding pay equity and competitiveness.
A company ratio that is too high could indicate that an organization is paying employees more than what is typical for similar organizations, which could potentially have a negative effect on profits and the overall compensation strategy. On the other hand, a low compa-ratio might signal that employees are underpaid, which could lead to high turnover and difficulty in attracting talent. Regardless of the situation, it's necessary to comprehend the factors for making informed decisions about compensation.
The Purpose of Compa-Ratio
Compa-ratio serves several important purposes in the realm of employee compensation. First and foremost, it helps organizations evaluate pay rates in relation to range midpoints, thereby enabling the identification of potential pay disparities within the organization and promoting internal pay equity. This is vital for guaranteeing fair compensation to employees in accordance with market standards, thus cultivating a positive work environment and enhancing employee retention.
Another key function of a compa-ratio is its role in informing compensation strategies. Organizations can gauge the competitiveness and fairness of an employee's remuneration by examining his/her salary in relation to the midpoint of a specific salary range. This information can then be used to:
- Make adjustments to their pay policy
Ensure that employees are rewarded appropriately for their contributions to the organization
- Maintain a competitive edge in the job market.
Compa-Ratio Example
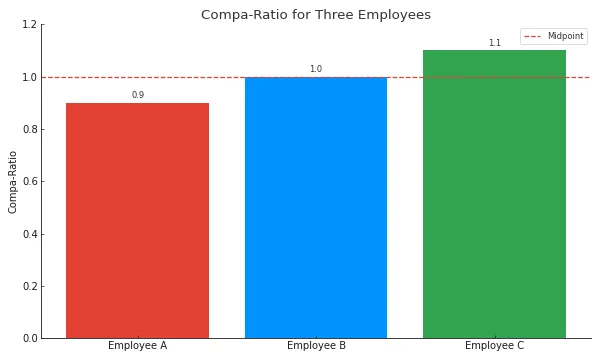
The infographic visualizes the Compa-Ratio for three hypothetical employees.
In the example above we can see the following examples:
Employee A has a Compa-Ratio of 0.90, indicating their salary is below the midpoint of the salary range.
Employee B is right at the midpoint with a Compa-Ratio of 1.00.
Employee C has a Compa-Ratio of 1.10, indicating their salary is above the midpoint.
Calculating Compa-Ratio: Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating the compa-ratio is a fairly straightforward process. The first step is to establish pay grades or pay bands for all job descriptions and roles in an organization. Once these have been established, compa-ratios can be calculated for individual employees, groups of employees, or even the organization as a whole. Organizations can gain valuable insights into their compensation strategies and make informed decisions by comprehending the various types of compensation and their applications.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the step-by-step process of calculating individual and group compa-ratios. Mastering the calculations for these types of compa-ratios will guarantee that your organization's compensation strategy relies on data-driven insights, leading ultimately to fair and equitable pay for all employees.
Individual Compa-Ratio Calculation
To calculate an individual compa-ratio, simply divide the employee's salary by the salary range midpoint for their job. This will provide you with a percentage value that represents how the employee's salary compares to the industry average for their role. A compa-ratio of 100% indicates that the employee's salary is perfectly aligned with the market average or market midpoint, while a higher or lower percentage signifies that their pay is above or below the market rate, respectively.
Individual compa-ratios are particularly useful during performance appraisals, as they can help managers and HR personnel determine the appropriate amount to reward employees who exceed work expectations. Using compa-ratios in this context enables organizations to ensure fair and competitive compensation for high-performing employees, thereby fostering a positive work environment and improved employee retention.
Group Compa-Ratio Calculation
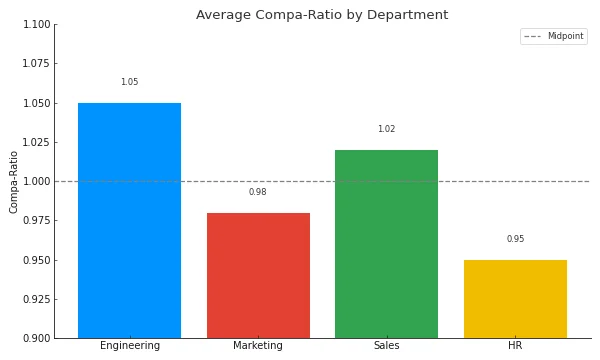
Group compa-ratios offer a broader perspective on employee compensation, including variable pay, by comparing the total salary of a group of employees to the sum of their respective job midpoint rates.
The chart above represents a group compa-ratio with the following characteristics:
- Engineering has an average Compa-Ratio of 1.05, suggesting that on average, the salaries in this department are above the midpoint.
Marketing has an average Compa-Ratio of 0.98, indicating that the department's average salary is slightly below the midpoint.
Sales has a close-to-midpoint average Compa-Ratio of 1.02.
- HR has an average Compa-Ratio of 0.95, which means the average salary in this department is below the midpoint.
To calculate the group compa-ratio, follow these steps:
- Sum the actual salaries of all employees in the group.
- Sum the job reference point rates for each role in the group.
- Divide the total salary by the sum of the job reference point rates.
To calculate the compa ratio, use the compa ratio formula which will give you the group compa-ratio.
This provides valuable insight into potential pay disparities among employee groups in terms of:
- gender
- ethnicity
- age
- other instances of conscious or unconscious bias
Organizations can ensure that their compensation strategies are fair and equitable for all employees by identifying and addressing these disparities.
Furthermore, group compa-ratios can be useful for:
- Budgeting purposes
- Assessing the effectiveness of remuneration policies
- Helping organizations make informed decisions
- Maintaining a competitive edge in the job market.
Analyzing and Interpreting Compa-Ratios
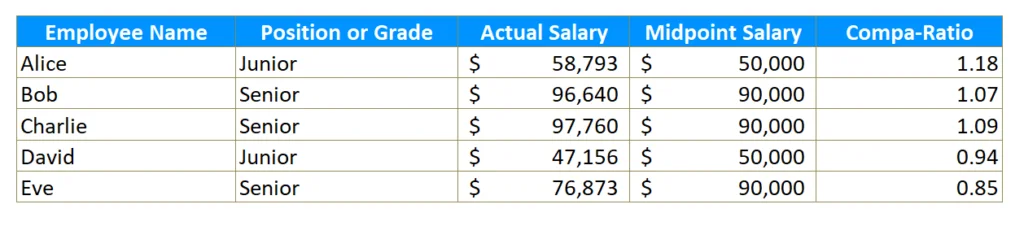
Compa-ratios are valuable tools for analyzing and interpreting employee compensation within an organization. It is generally advised that compa-ratios be maintained between 80% and 120%. Within this range, the organization can ensure fair and competitive remuneration for employees while upholding pay equity and competitiveness.
However, factors such as experience, skill level, or tenure may influence how an employee is paid within the optimal compensation range. For example, an average compa-ratio of 1.05 suggests that employees are receiving salaries 5% higher than the industry standard midpoint. This could indicate that the organization is paying its employees competitively, potentially leading to higher employee satisfaction and retention.
On the other hand, a compa-ratio below the recommended range may signal underpayment and the need for adjustment to maintain competitiveness and retain talent.
Compa-Ratio Ranges and Their Significance
Compa-ratio ranges are crucial indicators of how an employee's pay compares to market rates and can highlight potential pay policy issues. For instance, a company ratio below 80% may suggest that an employee is underpaid compared to the market average for their role, which could lead to dissatisfaction and high turnover. Conversely, a compa-ratio above 120% could indicate overpayment, potentially affecting the organization's profitability and overall compensation structure.
Organizations can identify potential issues with their pay policies and implement necessary adjustments to ensure paying employees fairly in line with market standards by analyzing compa-ratio ranges and their significance. This not only contributes to a positive work environment, but also helps attract and retain top talent in today's competitive job market.
Implementing Compa-Ratio in Compensation Strategies

Incorporating compa-ratios into compensation strategies is essential for ensuring fair and competitive pay. The process begins with setting up salary ranges based on industry benchmarks and job descriptions. Once salary ranges have been established, compa-ratios can be calculated and analyzed to inform various aspects of a company's compensation strategy, such as determining pay raises and adjustments based on market trends and employee performance.
Organizations can achieve internal pay equity, address pay disparities, and ensure fair rewards for employees' contributions by incorporating compa-ratios into compensation strategies. In the following sections, we will discuss how to establish salary ranges and determine pay raises and adjustments using compa-ratios.
Establishing Salary Ranges
Establishing salary ranges is a crucial first step in implementing compa-ratios in compensation strategies. Salary ranges should be based on industry benchmarks and job descriptions, ensuring that organizations maintain competitive compensation structures. Compa-ratios can be used to calculate salary ranges by comparing the salaries of similar positions in the same industry.
Having clearly defined salary ranges allows organizations to assess and interpret compa-ratios, identifying any disparities in pay between similar roles and ensuring that salaries are in line with the market. This data can then be used to inform compensation decisions, such as pay raises and adjustments, ultimately leading to a fair and equitable pay structure for all employees.
Determining Pay Raises and Adjustments
Compa-ratios play a key role in determining pay raises and adjustments, ensuring that employees are compensated fairly and in line with market standards. If an employee's company ratio is below the target ratio, it may be advisable to provide a pay raise or adjustment to bring it closer to the target ratio. Conversely, if the company's ratio is above the target ratio, it may indicate that the employee's salary is higher than market value, and adjustments may not be necessary.
Organizations can ensure appropriate rewards for their employees' contributions and maintain a competitive edge in the job market by using compa-ratios to guide pay raise and adjustment decisions. This data-driven approach helps promote a positive work environment, improve employee satisfaction, and ultimately, retain top talent.
Addressing Pay Equity with Compa-Ratios
Compa-ratios can be instrumental in addressing pay equity within an organization. Organizations can ensure equitable compensation for all employees, regardless of gender, race, or other factors, by identifying pay disparities and implementing fair pay practices.
Group compa-ratios, in particular, can be used to identify potential pay inequality within an organization. In the following sections, we will discuss how to identify pay disparities using group compensation ratios and implement fair pay practices to ensure equitable compensation for all employees.
Identifying Disparities
Group compa-ratios can provide valuable insight into potential pay disparities among employee groups in terms of gender, ethnicity, age, or other factors that may be subject to conscious or unconscious bias. Organizations can identify any discrepancies in pay that may require further investigation by comparing the average pay of a subgroup of employees with a larger category of employees, such as women versus men or minorities versus all employees.
Once these pay disparities have been identified, organizations can use this information to make necessary adjustments to their compensation strategies, ensuring that all employees are compensated fairly and equitably. This not only contributes to a positive work environment, but also helps attract and retain top talent in today's competitive job market.
Implementing Fair Pay Practices
Implementing fair pay practices based on compa-ratio analysis ensures that employees are compensated equitably, regardless of gender, race, or other factors. Organizations can make informed decisions about pay adjustments and ensure fair pay for all employees by analyzing compa-ratios and identifying pay disparities.
Fair pay practices can include adjusting salary ranges, determining pay raises and adjustments, and addressing pay equity. By implementing these practices, organizations can create a positive work environment, improve employee satisfaction, and ultimately, retain top talent in today's competitive job market.
Alternative Methods to Measure Pay Competitiveness
While compa-ratios serve as an effective tool for gauging pay competitiveness, alternative methods exist that organizations can utilize to gain additional insights into employee compensation and market trends. These methods include market-ratio, target percentile, and range penetration.
Market-ratio is determined by dividing the current salary by the market equivalent, providing a measure of the competitiveness of a given compensation package relative to the market. Target percentile indicates the amount of money set aside to attract qualified personnel in a particular field or industry and is utilized to determine the suitable salary range for a position.
Range penetration, on the other hand, refers to an individual's salary relative to the total pay range for the position or similar positions within the organization and is calculated using the formula: Range penetration = (salary – range minimum) / (range maximum – range minimum).
By employing these alternative methods, organizations can gain a more comprehensive understanding of their compensation structures and make data-driven decisions accordingly.
Summary
In conclusion, companies play a crucial role in ensuring fair and competitive pay in today's job market. By understanding and leveraging compa-ratios, organizations can establish fair compensation structures, address pay disparities, and make informed decisions about pay raises and adjustments. Additionally, alternative methods such as market-ratio, target percentile, and range penetration can provide further insights into employee compensation and market trends.
As the job market continues to evolve and competition for top talent intensifies, it is more important than ever for organizations to ensure fair and equitable pay for all employees. By mastering the concept of compa-ratio and applying it to compensation strategies, you can contribute to a positive work environment, improve employee satisfaction, and ultimately, retain the talent needed to succeed in today's competitive landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a compa-ratio of .75 mean?
A compa-ratio of 0.75 means an employee is paid 25% below the market average, indicating they may be more likely to seek employment with competitors at a higher rate.
This can lead to higher turnover rates and a decrease in employee morale, which can have a negative impact on the company's bottom line.
What does 95% compa-ratio mean?
Compa-ratio of 95% is above the 80-90% range, indicating that the individual is a fully competent performer fulfilling the job as defined.
This suggests that the individual is performing at a high level and is likely to be rewarded accordingly.
What does a compa-ratio of 1.0 mean?
A compa ratio of 1.0 signifies that the employee is being paid the same amount as the midpoint salary range for their position, meaning they are receiving 100% of the rate.
This is an important metric for employers to consider when evaluating the salaries of their employees. It can help them determine if they are paying their employees fairly and competitively. It can also help them identify any discrepancies in pay between employees of different genders, races, or other demographics.
What is a good compa-ratio?
A good company ratio is between 80% to 120%, meaning the employee is paid at the target market position, or the median salary of their role.
This indicates that they are being paid competitively when compared to other organisations in the same industry.
What is the optimal compa-ratio?
The optimal compa-ratio is between 80-120%, with a target of 100% indicating market median salaries for competitive employees.
